Molecular Microbiology
On the Possible Ecological Roles of Antimicrobials
Introduction of antibiotics into clinical use in the middle of the 20th century has had a profound impact on modern medicine and human wellbeing. The contribution of these wonder molecules to public health and science is hard to overestimate. Much research has informed our understanding of antibiotic mechanisms of action and resistance at inhibitory concentrations in the lab and in the clinic.
Antibiotics, however, are not a human invention as most of them are either natural products produced by soil microorganisms or semisynthetic derivatives of natural products. Because we use antibiotics to inhibit bacterial growth, it is generally assumed that growth inhibition is also their primary ecological function in the environment. Nevertheless, multiple studies point to diverse non‐lethal effects that are exhibited at lower levels of antibiotics. Here we review accumulating evidence of antibiosis and of alternative functions of antibiotics exhibited at subinhibitory concentrations.
We also speculate on how these effects might alter phenotypes, fitness, and community composition of microbes in the context of the environment and suggest directions for future research.
Enlace al trabajo desde la ULE
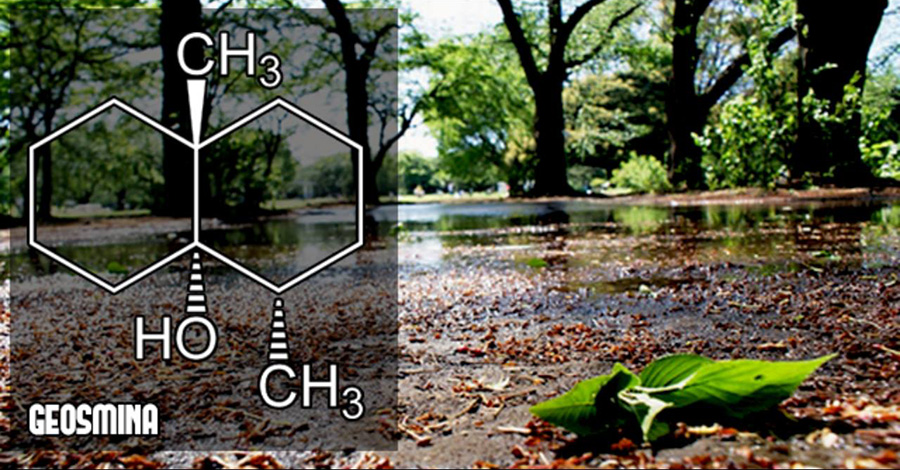
Streptomyces, colémbolos y geosmina
Tomado y ampliado a partir de ABC y la publicación original Cuando llueve las primeras gotas que caen sobre un suelo seco favorecen que s...
-
Artículo de Pedro Gargantilla en ABC. El Dr. Gargantilla es médico internista del Hospital de El Escorial (Madrid) y autor de varios libro...
-
Tomado y ampliado a partir de ABC y la publicación original Cuando llueve las primeras gotas que caen sobre un suelo seco favorecen que s...